1. 概述
我们在使用 SpringMVC 开发业务逻辑的时候,经常使用@Controller,@RequestMapping 等注解快速注册并接收网络请求。
那今天我们来看一下,当接收到一个网络请求后,SpringMVC 框架是如何找到你的业务逻辑代码处理请求,并返回结果的。
2. 核心类图及方法
SpringMVC 处理请求的核心类是 DispatcherServlet,我们先来看一下他的类图
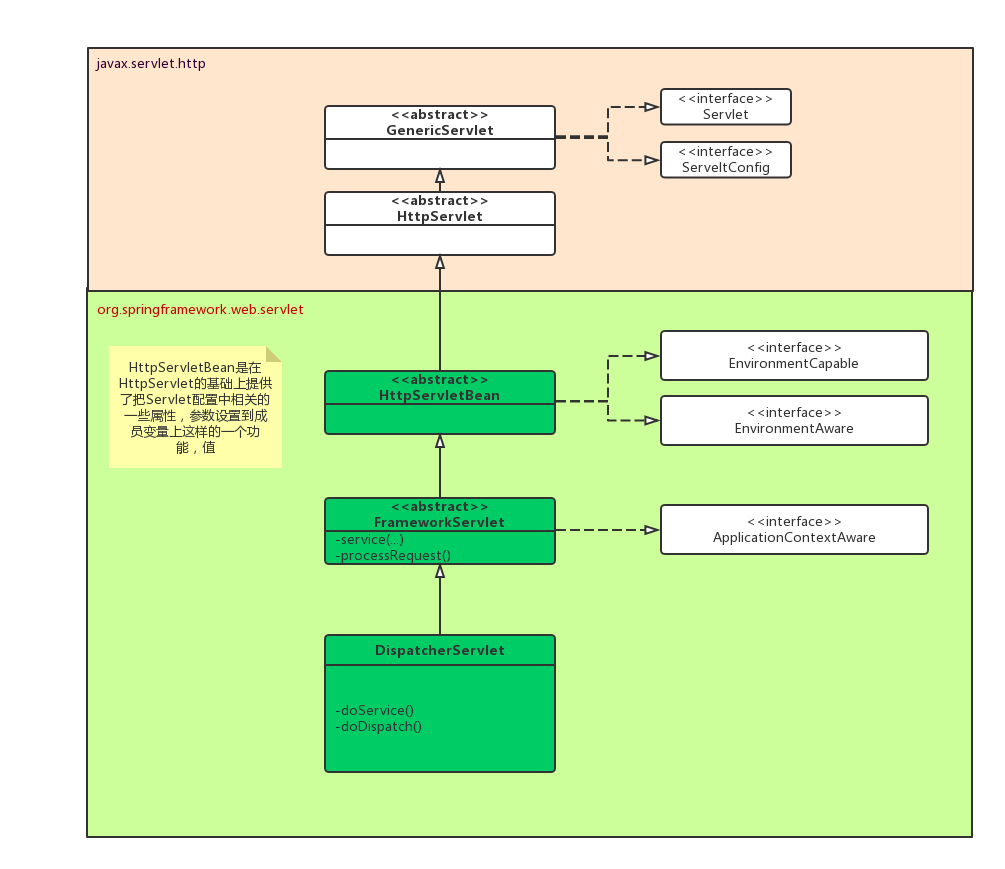
我们看到核心类 DispacherServlet 的祖先都是一些个抽象类。真正可以被实例化使用的只有 DispatcherServlert,那关于处理请求方面,
这些抽象类都干了些什么呢?我们先来看一下定义了 Servlet 容器的接口javax.servlet.http.Servlet的源码
2.1 Servlet 接口 及 HttpServlet 中的实现
1 | public interface Servlet { |
在这里我们主要关心的是处理请求的 service 方法,我们来看一下他在HttpServlet中的实现。
1 | protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) |
可见 HttpServlet 实现了 service 方法并根据 Http 请求的 Method 调用了 doGet,doHead,doPost,doPut,doDelete,doOptions,doTrace 等方法。那末,请求便根据 requestMethod 被分散到了不通的方法中处理。
2.2 FrameworkServlet
我们再来看一下 DispatcherServlet 的父类 FrameworkServlet 的源码
1 | /** |
FrameworkServlet 做了以下几件事情:
- 覆写 doGet,doPost,doPut 等方法,都调用了 processRequest 来处理请求,把父类 HttpServlet 分散到各个方法中处理的请求又归拢到了一起,使用 processRequest 集中处理。
- 覆写 service 方法,支持了 http PATCH 方法。
- processRequest 方法初始化了 ContextHolder 并调用了抽象方法doService处理请求。
- publish 了请求已被处理的 ApplicationEvent。
2.3 DispatcherServlet
DispacherServlet 实现了父类的抽象方法 doService。先做了一些准备工作,便调用了 doDispatch 处理请求。
1 | /** |
DispacherServlet 的 doDispatch 方法是 SpringMVC 处理请求的核心方法,我们来看一下源码:
1 | /** |
处理步骤:
- 获取请求对应的 HandlerExecutionChain,HandlerExecution 中的 handler 记录了业务代码的入口方法。
- 获取该 HandlerExecutionChain 中 handler 对应的 handlerAdapter
- 执行 HandlerExecutionChain 中拦截器的 preHandler 方法。
- 执行 hander,获得 ModelAndView 对象 mv
- 执行 HandlerExecutionChain 中拦截器的 postHandler 方法。
- 执行 postDispatchResult 方法,如果 mv!=null,渲染视图。
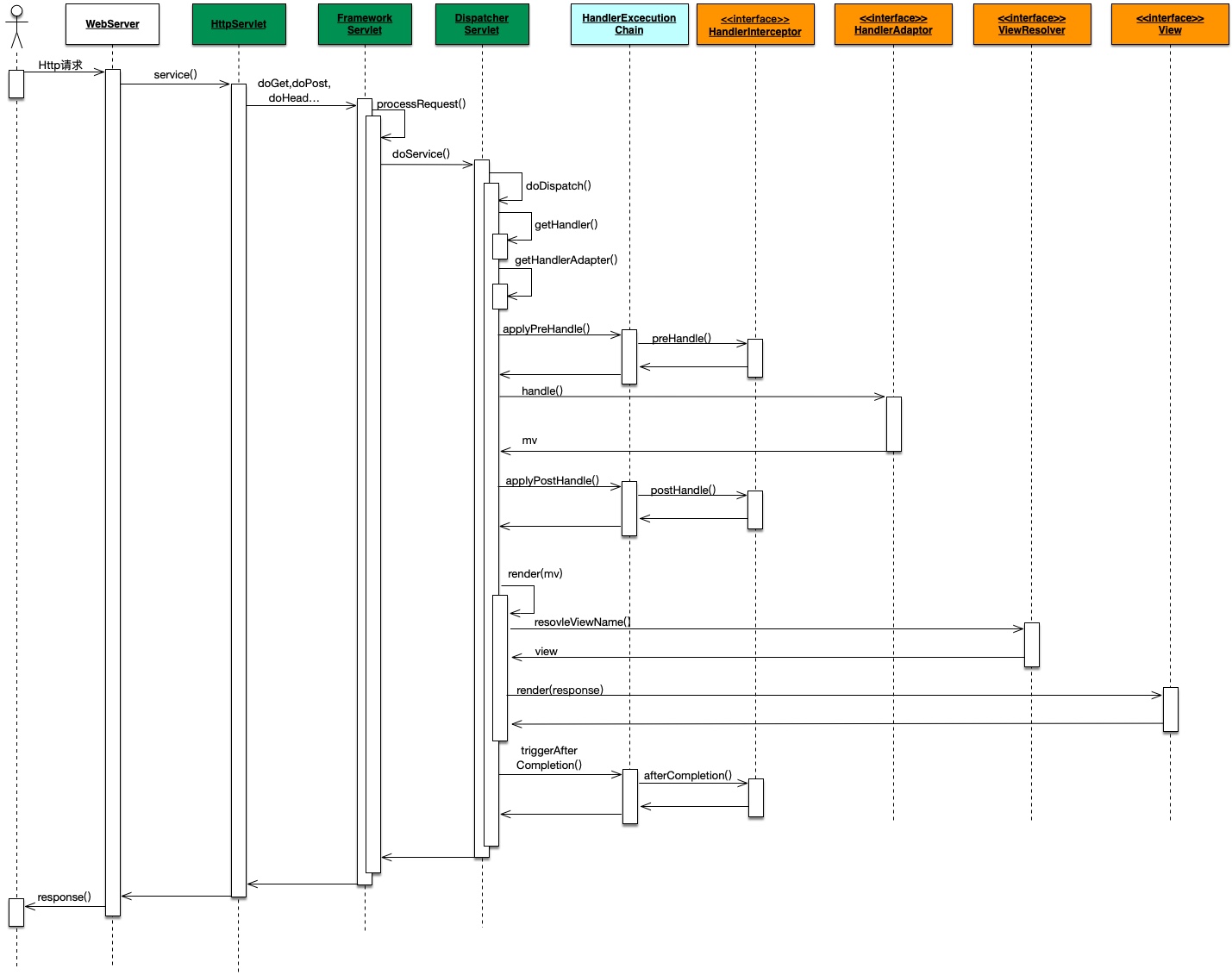
3. 总结
整个请求的处理流程的时序图如下:
下一篇:
