1 获取 HandlerExecutionChain
DispatchServlet 的 doDispatch 方法中调用了 getHandler 方法获取了执行请求的 HandlerExecutionChain。
HandlerExecutionChain 包含了拦截器已经处理该请求的 handler 等信息。
来看一下 doDispatch 的源码片段
1 | protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { |
1.1 获取 HandlerExecutionChain
在来看一下获取 HandlerExecutionChain 实例 mappedHandler 的方法 getHandler
1 |
|
这个方法,for 循环了 this.handlerMappings 列表,当列表中的 HandlerMapping 元素 hm 能取到 handler 则立即返回。
那么这个类属性列表 this.handlerMappings 如何初始化的呢?
我们来看一下它的初始化方法 DispatcherServlet.initHandlerMappings
1 | private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { |
因为 this.detectAllHandlerMappings 默认为 true 所以初始化方法从 ApplicationContext 里获取了所有继承
HandlerMapping 接口的 bean,并把它加入到了 handlerMappings 中。
SpringBoot 为我们默认注入了一下几个 geHandlerMapping 的实现类
- SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping
- BeanNameUrlHanderMapping
- WebMvcConfigurationSupport
- WelcomePageHanderMapping
限于篇幅,这里将重点分析我们常用的 RequestMappingHandlerMapping。
Springbooot 框架中 ,RequestMappingHandlerMapping 是在哪里被注入的呢?
是在 spring-boot-autoconfigure 包中的 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 里注入的。
1 |
|
1.2 RequestMappingHandlerMapping,构建所有@RequestMapping 接口的注册表
RequestMappingHandlerMapping 实例中构建了一个 所有@RequestMapping 接口的注册表,我们来看一下它的初始化构建过程。
1.2.1 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 类图
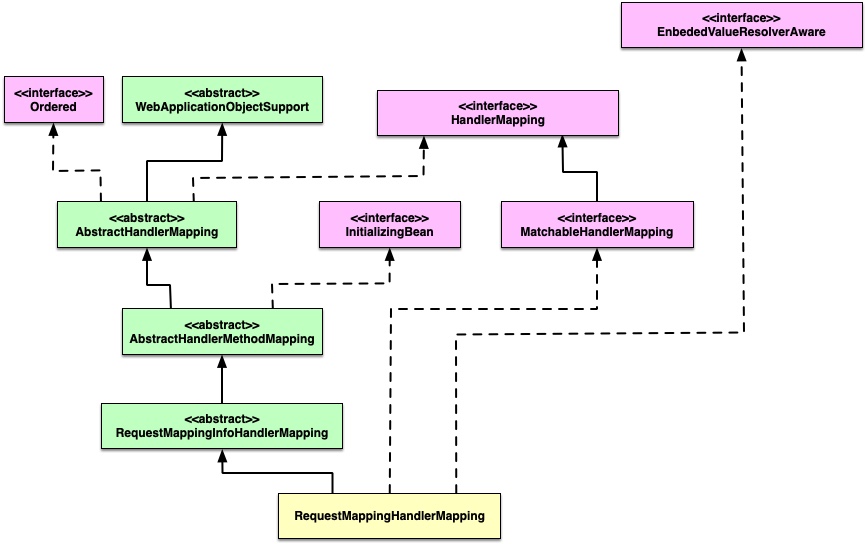
1.2.2 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 初始化
RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的父类 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 实现了 InitializedBean 接口。
在 spring 初始化 bean 的时候,如果 bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,会自动调用 afterPropertiesSet 方法。
来看 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法:
1 | public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping |
在做了一些配置之后调用了祖先 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的 afterPropertiesSet() (父类 RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping 没有相应实现)
1 | public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean { |
1 | public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping |
这里调用了 initHandlerMethods 来查找所有 Handler 的方法。
- 第一步把 ApplicationContext 里所有的 bean 的名称全部去出来。
- 根据 bean 的名称获取 bean 的类型 beanType
- 调用 isHandler 判断是否是 Handler,
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的 isHanlder 方法,根据类型是否有@Controller 或
@RequestMapping 注解判断是否是 Handler - 如果是 Handler 调用 detectHandlerMethods 注册所有的 handler 方法。
我们来看一下 detectHandlerMethods 方法
1 | public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean { |
1 | public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping |
1 | public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) { |
detectHandlerMethods
- 先调用了 MethodIntrospector.selectMethods。MethodIntrospector.selectMethods 的第二参数传入了一个 filter 函数。当返回不是 null 的时候,将会把返回结果保存在 Map<Method,T>中。
- filter 中调用了 getMappingForMethod 方法,传入 method 和 该方法所在类 handlerType
- 调用 createRequestMappingInfo 传入 method,如果这个方法被@RequestMapping 注解修饰,就会返回一个 RequestMappingInfo 实例,RequestMappingInfo 实例记录接口 method 处理 HttpRequest 的所有信息,包括路径,接口允许的方法,CORS 信息,已经各种限制条件。
- 如果返回实例不为 null,再次调用 getMappingForMethod 方法,传入该方法所在类型 handlerType 获得一个基于类的 RequestMappingInfo 实例,
- 两个实例 merge 得到一个新的 RequestMappingInfo 实例。(请求路径的合并等。。)
- 得到所有 methods 的 map 以后进行遍历,调用 registerHandlerMethod 进行注册保存。
- 调用了 this.mappingRegistry.register 进行注册。保存了 mapping(requestMappingInfo)和 handlerMethod 的关系,
以及 urlString 与 mapping(requestMappingInfo)的关系。
1.2.3 初始化总结
在完成了 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的初始化以后,这个实例中便保存了我们所有@RequestMapping 修饰的接口信息。
1.3 RequestMappingHanderMapping 获取 handlerChain
我们回到文章的第一段代码
1 | protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { |
handlerMapping 调用了 getHandler(request)获取 HandlerExecutionChain 实例,那么我们来看一下
RequestMappingHanderMapping 的 getHandler 方法。
1 | public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport implements HandlerMapping, Ordered { |
调用了 getHandlerInternal,
从 mappingRegistry 中获取匹配路径的 mapping,并排序获取最匹配的 handlerMethod
1 | public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean { |
获取到了 handlerMethod 以后调用了 getHandlerExecutionChain 把匹配的 Intercepters 组装成了 HandlerExecutionChain 对象
1 | protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) { |
2. 获取 HandlerAdapter
回到 doDispatchServlet 的代码片段
1 | // Determine handler adapter for the current request. |
调用了 getHandlerAdapter 获取 HandlerAdapter 实例 ha。
DispatchServlet 初始化的时候会把 appContext 里所有实现了 HandlerAdapter 的 bean 添加到 this.handlerAdapters 里,
然后通过 for 循环查找支持传入的 handler 的 HanderAdapter。支持 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 的是
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter。
1 | protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException { |
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 的 support 方法,如果 handler 的类型是 HandlerMethod 即支持,RequestMappingHandlerMapping 返回的 handler 类型就是 HandlerMethod
1 |
|
3. HandlerAdapter 执行 handler 方法。
回到 doDispatchServlet 的代码片段,获取 ha 以后,先调用了 preHandle 里的 interceptors,如果返回是 true,
则执行了 ha.handle,执行了 handler。
1 | ... |
3.1 RequestMappingHandlerAdapterd 的 handler 方法
1 |
|
handlerInternal 调用了 invokeHandlerMethod 执行 handlerMethod
1 |
|
invokeHandlerMethod 组装了两个实例,
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 对象 invocableMethod 和 ModelAndViewContainer 对象 mavContainer
把一堆必要的信息传递给了 invocableMethod,比如参数解释器 this.argumentResolvers,返回值处理器 this.retrunValueHandler 等。。。
然后调用了方法 invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
1 |
|
invokeAndHandle 调用了 invokeAndHandle 处理请求,如果返回值为空且请求被处理则调用 mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true)后返回。
如果返回值不为空则使用 this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue 处理返回值。
1 | public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, |
getMethodParameters 先调用了方法 getMethodArgumentValues(),getMethodArgumentValues 里为每一个参数检查是否有支持的参数解释器 argumentResovler,如果有的话则装备一个参数实例。如果找不到 methodResolver 的话就抛出异常。
得到参数列表 args 以后调用 doInvoke()方法。
1 | public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, |
doInvoke 调用了 getBridgedMethod().invoke(getBean(), args) 执行了我们用@RequestMapping 修饰的方法,并返回了结果。
1 | public class InvocableHandlerMethod |
